|
Case Of Covid 19, Looking At Virus Harmful To Plants
14/08/2021
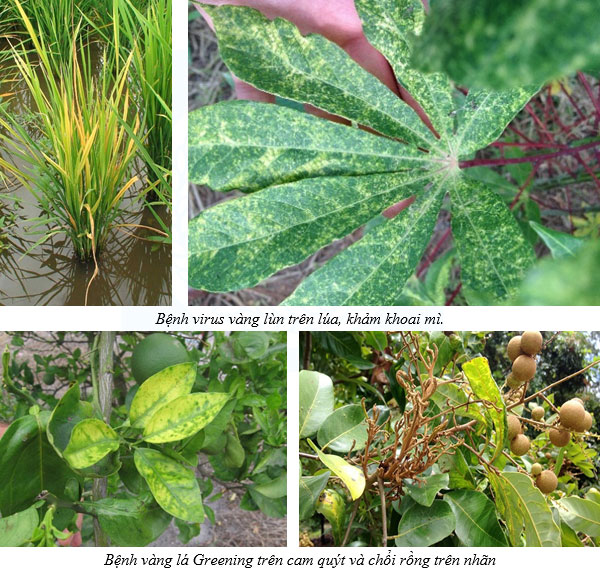
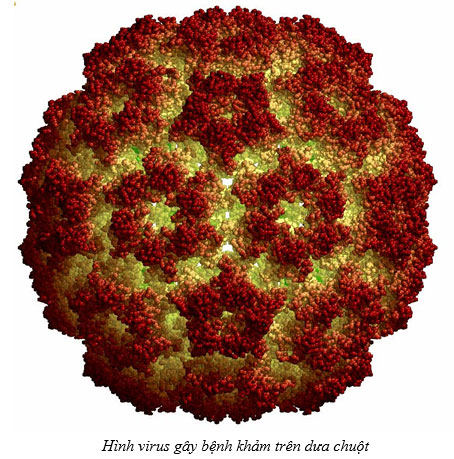
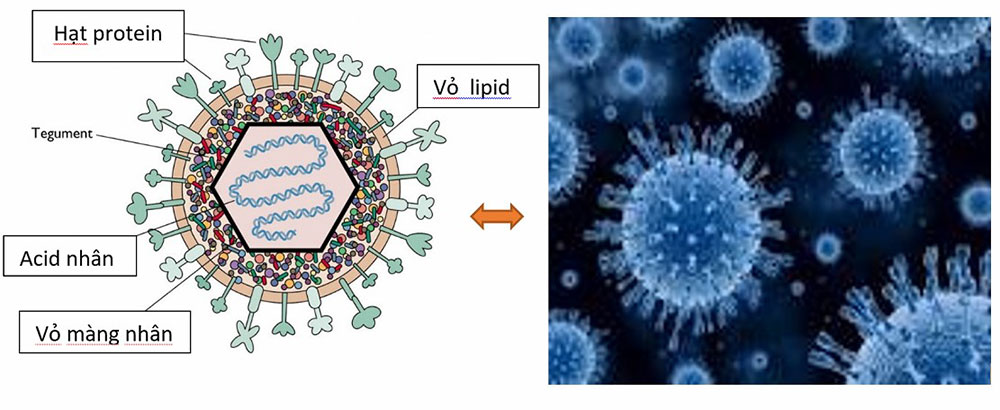
MSc Huynh Kim Ngoc What are viruses? Viruses are biological units with very small size, no cell structure, average diameter from 20 to 300 nm (1 nm = 1/1,000,000 mm), which can only be seen through a electron microscope. Viruses can cause disease in humans, animals and plants. Viruses cannot live or grow in artificial environments, but must parasitize in the cells of humans or animals and plants that are suitable for them. Structure of the virus: Viruses have a very simple structure: The inner core is a nuclear acid (DNA, RNA), is by a shell composed of lipids, on which small protein particles are attached, so the virus is susceptible to infection. destroyed if exposed to alcohol (alcohol), alkali (savone) or high temperature. Harmful way: Viruses are obligate intracellular parasites because they can only live and multiply in the host is living cells. This process proceeds as follows: Once entering the host cell, the virus that causes the disease will multiply rapidly by taking the nuclear acids, lipids, and proteins of the host cell to make its own cellular material. Host plants have metabolic disorders and show disease symptoms to the outside. Viral diseases of plants: Viruses cause damage to many crops such as diseases of dwarf yellow rice, leaf curl dwarf , weedy rice (transmitted by planthoppers), cassava leaves mosaic disease (pathogen: whitefly), Greening on citrus (pathogens are Diaphorina citri), mosaic diseases on gourds, squash, melons, chili peppers, tobacco, papaya, sugarcane white leaf disease, Legionnaire is disease damages longan (Mycoplasma) etc.. The causative agent of the mosaic disease are insects that belong to the group of suckers such as aphids, thrips, whiteflies, spiders, etc. Spread and transmission of diseases: Viruses cannot spread to a large area by themselves. In humans, the virus is spread by surface contact, by inhalation, by needles, by blood transfusion, etc. In plants, the virus is transmitted by many routes: (1) through vectors. , mainly through sucking insects, (2) through cutting tools, pruning or mechanical wounds between diseased leaves and roots and healthy plants, (3) through asexual propagation such as cuttings, tubers, branches, roots, ... (4) through a few seeds of vegetables, tomatoes, beetroots, (5) through the soil (potato mosaic), (6) through fungi, nematodes, etc. However, the disease does not spread through water , air
Symptom: The symptoms of viral diseases on plants are very diverse, depending on the cultivar, the time of infection, the cultivation conditions, the soil, the weather, the health status of the plants, etc. which symtoms manifest, severe or mild levels, affect productivity differently . In general, the sooner the disease is infected, the higher the yield is affected, the land is poor, the nutrient supply is poor, the trees are depleted, etc., the greater the loss .Symptoms of viral diseases on plants are very specific and easy to identify: If infected early, plants will be dwarf, stunted, stem grows lateral shoots, small leaves, shrunken veins, twisted, curved edges, torn, leaves turning green dark or light yellow, or alternating yellow-green, the leaf blade is not flat, rough, lumpy (mosaic). Rice with virus disease, plants with few grains, unfilled grains, cassava gets mosaic diseased with few tubers, fruits on diseased plants are small, deformed, poor quality, high fiber, less water.
Treatment: On crops, there is no cure for viral diseases, only indirect prevention and control by means of killing vectors, which are sucking insects such as hoppers , aphids, whiteflies, aphids, etc., with specific chemical products such as Osago 80WG, Sago super 20EC, Sec Saigon 25EC, SK Enspray 99EC mineral oil, etc. However, the most economical and effective measure is to use disease-free seeds, without taking tubers, cuttings, stems, and roots.. from infected plants to make seeds or grafts, pay attention not to plant thickly, plant in concentration, fertilize fully and balance, take care of healthy plants, in addition, it is necessary to visit the field regularly, especially in the period 1-2 months after planting, for early detection of diseased plants, uprooting and destruction, timely prevention and treatment with the above-mentioned special products, otherwise the disease will spread quickly and greatly affect the yield later.
|
To prevent, in addition to plowing and burying weed seeds, collecting weed stalks and stumps left after tilling the land to burn, not letting weeds produce seeds in production fields, etc., the use of chemical products is still a measure. optimal because of its ability to thoroughly kill weeds, reduce labor and take advantage of more time than manual weeding.
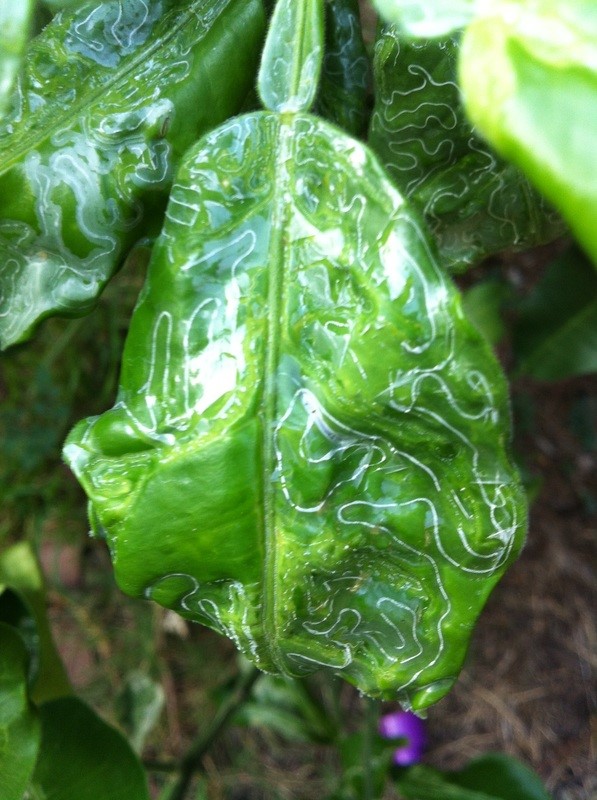
Miner has the scientific name Phyllocnistis citrella Staint., family Phyllocnistidae, order Lepidoptera. The miner occurs in many countries in the tropics and subtropics. The main host of the miner is the citrus family - Rutaceae. In addition, the miner also attacks mangosteen and some other plants.
Adult is a small planthopper, with a body 2-3 mm long, the whole body is ash gray, slightly greenish, the wings are opaque with many small brown spots.Eggs are oval, 0.3 mm long, have a pointed end and are attached directly to the leaf surface, leaf axils.
Green bugs specialize in the fruit of citrus groups (oranges, tangerines, lemons, grapefruits, kumquats...), some people call them orange bugs, or orange suckers. Their scientific name is Rhynchocoris poseidon or Rhynchocoris humeralis.
In Vietnam, yellow leaf curl disease is very common on papaya trees, especially the disease is often severe in areas of high and continuous planting, areas with hot and arid climates. The disease has significantly reduced the yield and quality of papaya. Gardens that are infected early when the plants are young may not yield. However, up to now, many gardeners still do not know the cause and how to fix it.
Spider mites are common pests on citrus trees, especially in hot and dry climates that are suitable for spiders to grow and cause severe damage.The group of harmful spiders is usually very small in size, unlike the natural enemy spiders.
This group includes species that are generally very small in size, causing damage by sucking plant sap (on leaves, fruits, branches, stems).
There are many species of mealybugs present on the group of Oranges,Tangerines,Grapefruits and Lemons (Citrus), which can be divided into 2 groups:
+ Group of sticky mealybugs with common varieties such as Lepidosaphes, Aonidiella, Coccus and Saissetia.
+ Group of flower mealybugs with common genera and species such as Pseudococcus, Planococcus and Icerya purchasi.
Dry branches and berries disease often appear to be common damage on coffee gardens during the rainy season. The disease causes death of branchs, dry fruit, severely affects the canopy structure and coffee yield if not paid attention to prevention.
Pink disease commonly causes diseases on rubber plantations in the rainy season, especially on garden from 4-8 years old. This year, rubber has to go through a period of severe drought, weakening the tree, so now in tnshe rainy season it is easy to get infected. Therefore, it is necessary to pay attention to good management to avoid affecting the garden.
In recent years, the area of citrus has been expanded because it is a fruit tree with high economic efficiency. However, in order to sell at a high price, not only in quality but consumers also require the external beauty of the fruit, so pest management on citrus is a matter of great concern to farmers. The hot season is a favorable condition for thrips to develop and cause damage, affecting the commercial value of fruit.
- Headquarters
- SAIGON PLANT PROTECTION JOINT STOCK COMPANY
- RQ 1, Nguyen Van Quy St., Tan Thuan Ward, HCM City
- Tax code: 0300632232
- Tel: (028) 38 733 295 - 38 732 077
- Fax: (028) 38 733 003 - 38 733 391
- Website: www.spchcmc.vn - Email: info@spchcmc.vn
- SAIGON PLANT PROTECTION COMPANY
- SAIGON PLANT PROTECTION JOINT STOCK ENTERPRISE
- Lot C1-C3 Hiep Phuoc Industrial Park, Hiep Phuoc Commune, HCM City
- Tel: (028) 3873 4089 - Fax: (028) 3873 4086
- Affiliated Unit
-
- Quick Links
- Home
- About us
- Career Opportunities